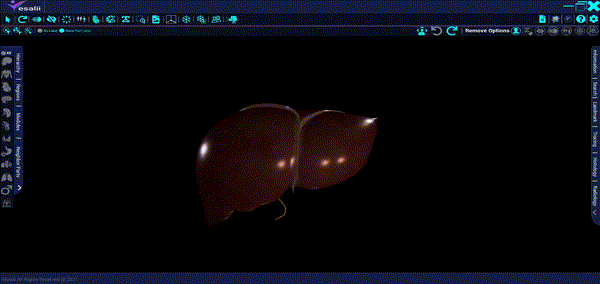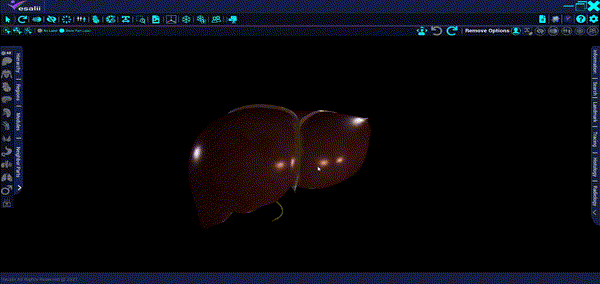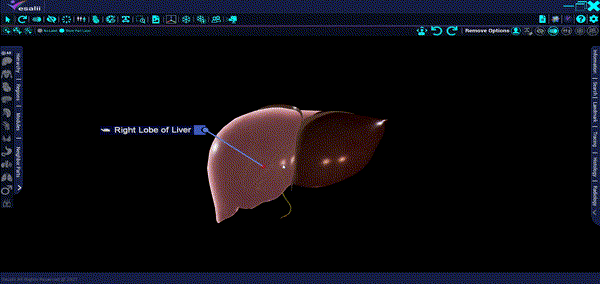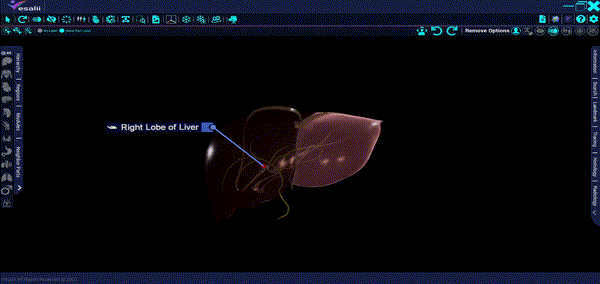
The liver is the largest gland in the body, filling a significant part of the upper abdominal cavity. The liver takes up the majority of the right hypochondrium and epigastrium and frequently expands into the left hypochondrium as far as the left anterior axillary line.
The liver is wedge-shaped and has a reddish-brown color that varies according to fat content. It carries out an extensive range of metabolic actions necessary for homeostasis, digestion, and immune defense, which are its main functions. The liver is responsible for the production and secretion of bile into the gastrointestinal tract and it is involved in many activities to metabolize carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
The liver also filters blood by removing foreign particles, such as bacteria, from the blood. Additionally, the liver produces an anticoagulant substance called heparin, performs detoxication functions, produces bile pigments, and secretes bile salts.